Geophysical survey of landslide movement and mechanism in Gorontalo Outer Ring Road, Gorontalo

Gorontalo Outer Ring Road (GORR) road section
Gorontalo infrastructure development focus on improving transport efficiency through the development of Gorontalo Outer Ring Road (GORR). The Government has set the cost 750 billion rupiahs for GORR and planned will be completed by 2019 but constrained by landslides. This research aims to reconstruct and identify the type and mechanism of a landslide at GORR. The result of this research is landslide type and mechanism in the research area. The method used is 2-dimensional electrical resistivity sounding with Wenner-Schlumberger configuration. Landslide mechanism is analyzed based on the resistivity value table on Vingoe resistivity value supported by geological data. Based on geophysical data, subsurface conditions showed blocks of limestone with a resistivity value about 132 ohm.m and marked red-purple colors. These blocks of limestone interpreted as the result of the weathering process and buried in weathered clastic limestone. Landslide movement type is sliding movement and concluded as a rockslide. There is a potential for subsurface landslide blocks occur caused by the weathering process on fractures in the research area. The future prevention steps are by increasing the surface water absorption by planting in the geotextiles or prevent water infiltration in the landslide area. In addition, manufacturing retaining wall is also required.
Usman, F. C. A., Manyoe, I. N., Duwingik, R. F., & Kasim, D. N. P. (2020, November). Geophysical survey of landslide movement and mechanism in Gorontalo Outer Ring Road, Gorontalo. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 589, No. 1, p. 012008). IOP Publishing.
Sekolah Geotermal

Buku Sekolah Geotermal
Dalam rangka meningkatkan pengetahuan dan kepedulian anak-anak di Desa Pentadio Barat terhadap geotermal dan lingkungan geotermal maka salah satu program yang dilaksanakan oleh mahasiswa KKN Restorasi Sungai dan Danau UNG tahun 2020 adalah Sekolah Geotermal.
Sekolah Geotermal adalah program pembinaan kepedulian dan kesadaran terhadap lingkungan geotermal Pentadio sejak dini bagi anak-anak SD di Desa Pentadio Barat. Melalui program Sekolah Geotermal, anak-anak di Desa Pentadio Barat diharapkan akan menjadi agen perubahan masa kini dan masa depan yang akan senantiasa menjaga lingkungan geotermal serta mengembangkan potensi geotermal di Pentadio.
Beu, J., ... [et al.]; editor, Manyoe I.N. & Hutagalung R. (2020). Sekolah Geotermal. UNG Press, Gorontalo.
Sekolah Danau

Buku Sekolah Danau
Dalam rangka meningkatkan kepedulian dan kecintaan anak-anak di Desa Lupoyo terhadap Danau Limboto maka salah satu program yang dilaksanakan oleh mahasiswa KKN Restorasi Sungai dan Danau UNG tahun 2020 adalah Sikola Bulalo atau Sekolah Danau. Buku Sikola Bulalo berisi kisah anak-anak SD di Desa Lupoyo tentang Danau Limboto. Semoga program Sikola Bulalo dapat menjadi program pembinaan yang berkelanjutan bagi anak-anak di pesisir Danau Limboto dan berdampak pada perubahan pola pikir dan pola sikap anak-anak terhadap Danau Limboto.
Kasa, N.A., ... [et al.]; editor, Manyoe I.N. & Hutagalung R. (2020). Sekolah Danau. UNG Press, Gorontalo.
Analisis Struktur Geologi Daerah Leato Selatan dan Sekitarnya, Kecamatan Dumbo Raya, Kota Gorontalo
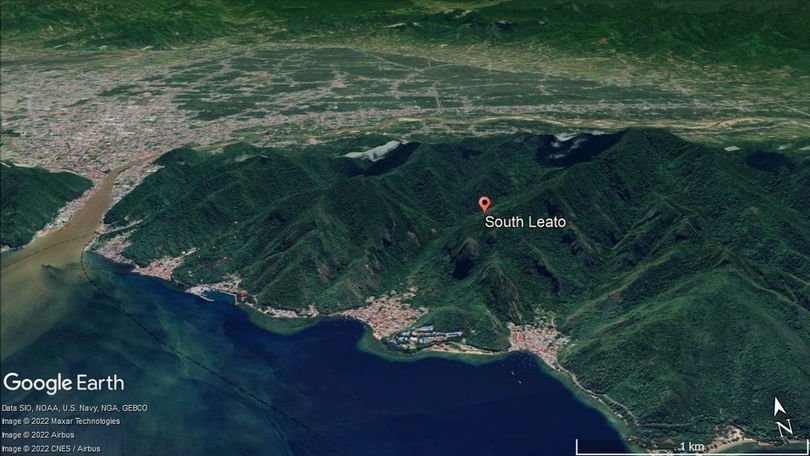
Research location.
The research area is located in South Leato, Dumbo Raya District, Gorontalo City. The research area is consist of Bone Diorite Formation which is in the miocene and the Pinogu Volcano Rock Formation which is in the quarter. The geological structure of the study area recorded in different rock formations is very interesting to be studied. The purpose of this study is to identify the types and general directions of geological structures that control the stress regime in the study area. This research method is in the form of field data collection and studio analysis. Data is collected by the field survey method. Analysis studio in the fracture processing data. Based on observations in the field, the geological structure contained in the study area is controlled by fracture. The type of fracture in the field is shear fracture. The results of the reconstruction of shear fracture in the study area is relatively northwest-southeast and north-south main direction.
Keywords: lithology, geological structures, rezim stress.
Madusila, R. S., Muhsin, N., Manyoe, I. N., Taslim, I., Umar, E. P., Abdullah, A. F., & Usman, F. C. A. (2020). Analisis Struktur Geologi Daerah Leato Selatan dan Sekitarnya, Kecamatan Dumbo Raya, Kota Gorontalo. Jurnal Azimut, 3(01), 1-7.
Subsurface Shallow Modelling Based on Resistivity Data in The Hot Springs Area of Libungo Geothermal, Gorontalo, Indonesia
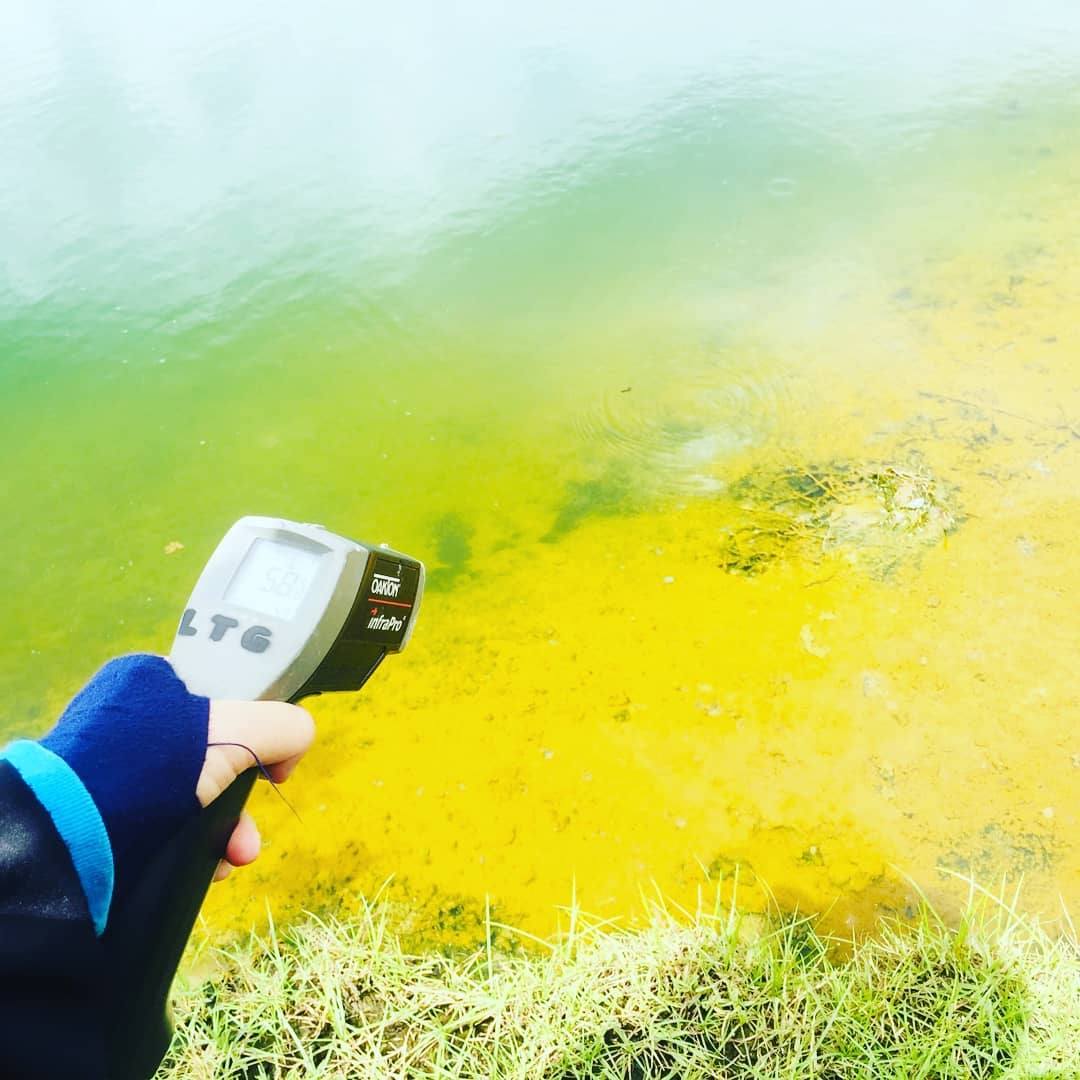

Libungo hotsprings
Volcano-tectonic events in Libungo can be the cause of the presence of geothermal potential. There is no detailed research on shallow subsurface conditions in Libungo that can show the distribution of subsurface fluids. This research aims to create a shallow subsurface model of the Libungo geothermal area based on resistivity data. Resistivity data collection was carried out in the Libungo hot springs area. The electrode configuration used is the Schlumberger configuration. The variation in resistivity values is calculated using current data, potential difference data and geometry factors. The results of the calculation of the resistivity values variation are plotted versus depth. Variations of resistivity value versus depth are then displayed in the form of a single log, lithology distribution and 3D lithology model. The results showed that the shallow subsurface of the Libungo geothermal area was composed of andesite, volcanic breccia, silty clay and clay. Andesite in the research area has resistivity values ranging from 320-349 ohm.m, has slightly fracture and is andesite dry. Volcanic breccia has a resistivity value of 177-198 ohm.m, has a well to slightly fracture and is a volcanic breccia moist. Silty clay has a resistivity value of 3.25-37.99 ohm.m and is a wet to moist silty clay. Clay has resistivity values in the range 1.56-2.78 ohm.m and is wet to moist clay. Fluid distribution in the shallow subsurface area occurs in volcanic breccia, silty clay and clay. Shallow subsurface fluids accumulate mostly in the northern part of the Libungo geothermal area.
Keywords: Fracture, Fluids, Thermal, Lithology, Schlumberger.
Manyoe, I. N., & Hutagalung, R. (2020). Subsurface Shallow Modelling Based on Resistivity Data in The Hot Springs Area of Libungo Geothermal, Gorontalo, Indonesia. Journal of Geoscience, Engineering, Environment, and Technology, 5(2), 75-80.
