Cara Registrasi Akun di Jurnal yang Menggunakan OJS 2
Sebelum menyerahkan naskah untuk diproses penerbitannya di suatu jurnal ilmiah, maka hal pertama yang harus dimiliki oleh penulis adalah AKUN yang akan digunakan untuk login di jurnal tujuan. pada tulisan ini, diberikan tutorial singkat bagaimana Cara Registrasi Akun di Jurnal yang Menggunakan OJS 2. Sebelum melakukan registrasi, anda hanya perlu menyiapkan email aktif yang akan digunakan untuk berkomunikasi. Pastikan email yang anda gunakan adalah email yang dapat diakses atau email yang sehari-hari anda gunakan untuk berkomunikasi. Berikut adalah tutorial tentang Cara Registrasi Akun di Jurnal yang Menggunakan OJS 2.
- Kunjungi website Jurnal Tujuan. Pada tulisan ini kami berikan contoh Jambura Journal of Mathematics yang menggunakan OJS 2.
- Klik menu Register pada bagian website jurnal

- Lengkapi data pada setiap kolom yang tersedia, mulai dari username, password, dst. Pada bagian afiliasi, sebaiknya ditulis lengkap mulai dari nama Program Studi, Fakultas, dan Universitas.
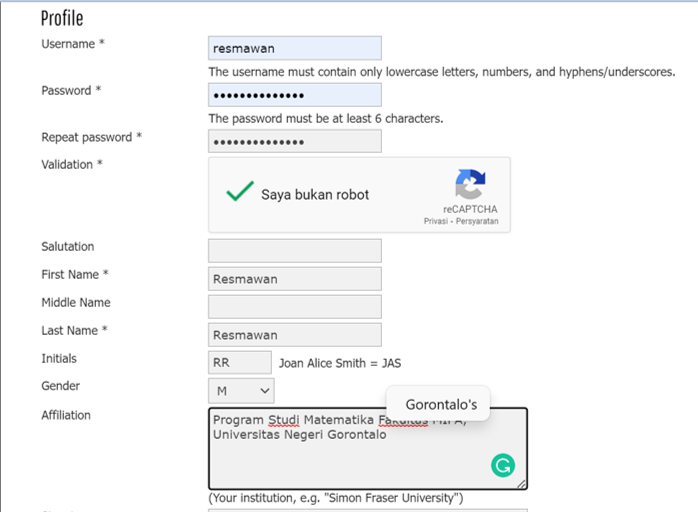
- Berikutnya yang perlu dipastikan terisi adalah kolom email dan konfirmasi email. Pada bagian akhir, jangan lupa untuk centang bagian register as AUTHOR. Jika ingin mendapatkan email notofikasi username dan password, silahkan centang CONFIRMATION.
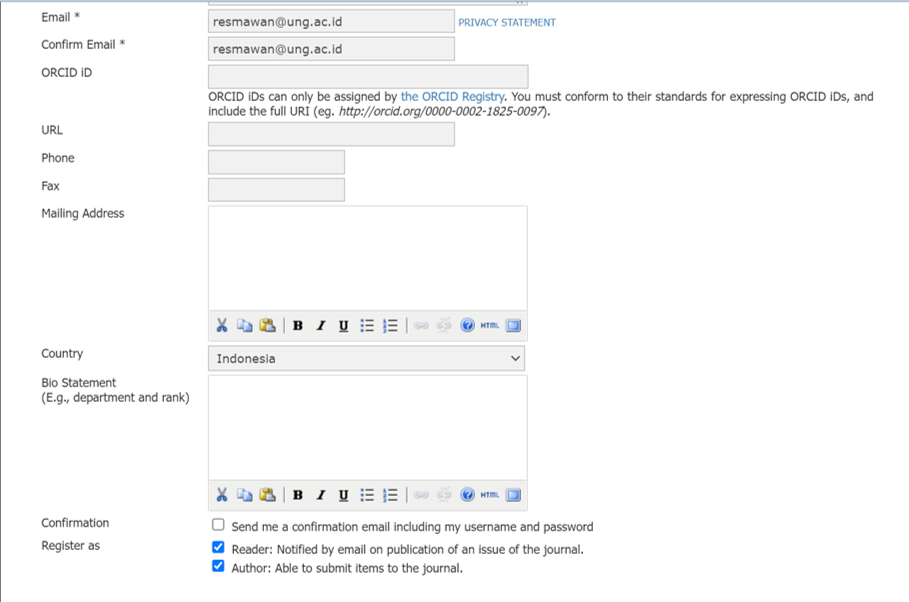
- Setelah semua data lengkap, klik tombol REGISTER, maka pendaftaran akun selesai.
- Sampai pada tahap ini, umumnya pendaftaran sudah selesai dan akun sudah bisa digunakan untuk login dan submit naskah. Namun pada beberapa jurnal, dibutuhkan verifikasi lebih lanjut agar akun dapat digunakan untuk login.
- Caranya, cek email verifikasi pada email yang digunakan untuk register. Jika tidak menemukan pada bagian inbox, biasanya terdapat pada kotak spam. Klik link verifikasi yang telah dikirimkan pada email, dan selanjutnya akun dapat digunakan untuk login.
Demikian Cara Registrasi Akun di Jurnal yang Menggunakan OJS 2, semoga bermanfaat. Berikut, kami mengundang anda untuk menerbitkan naskah dengan kualitas terbaik sesuai dengan scope beberapa jurnal kami berikut:
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF THE MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE SPREAD OF CHOLERA WITH VACCINATION STRATEGIES
Authors: Nur Safitri Abdul, Lailany Yahya, R Resmawan, Agusyarif Rezka Nuha
This research discusses the math model of spreading cholera disease with a mathematical strategy of math model constructed by considering a vaccination strategy. In addition, there is a population of hyper infectious and less infectious bacteria so the model of SVIR-BhiBli type, by. The model is formed in the form of determination of fixed point, determination of basic reproductions numbers, analyzing the equilibrium point and sensitivity analysis. The equilibrium analysis produces two equilibrium points of a immediate-free equilibrium point of aceletotic local if and endemic equilibrium points will be stable local asymptotics if . Furthermore, numerical simulation that the increase in vaccination rate influences on the decline in value while increased rate of vaccine depreciation can increase the value of . In addition, sensitivity analysis shows that if the parameter is enhanced while other contrast parameters will contribute to the increase in value, as a result can increase the rate of transmission of cholera disease. Whereas if the parameter is enhanced while other contrast parameters will contribute to the decrease in value, as a result of the dissemination of the disease can be pressed very significantly.
Published in Barekeng (SINTA 2)
GOODWIN MODEL WITH CLUSTERING WORKERS' SKILLS IN INDONESIAN ECONOMIC CYCLE
Authors: Sri Lestari Mahmud, Resmawan Resmawan, Sumarno Ismail, Nurwan Nurwan, Febriani Taki
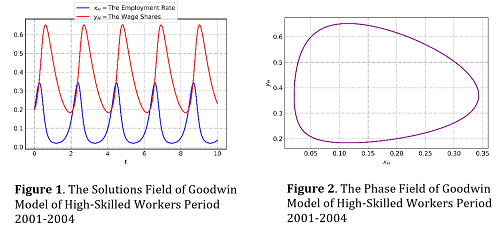
The economic model which deals with the economic cycle is Goodwin's Model. It presents the relationship between the employment rate and wage shares. In this study, the modification model was made, taking into three types of workers, namely high, medium, and low-skilled workers. Studies of the model are conducted by determining the equilibrium point and its stability analysis. Furthermore, a numerical simulation is given to see which model satisfies the ideal of Goodwin‘s model cycle prediction by using Indonesian data from 2000 to 2020. In the end, an investigation into the effects of reducing the wage gap between the three types of workers was conducted. The results showed two equilibrium points, namely The Equilibrium Point without Employment Rate and The Wages Share (T1) and the Existence Equilibrium Point of Employment Rate and Wages Share (T2). T1 achieves a stable node condition when ScQ<d+pi+et while T2 reaches a stable center condition when ScQ>d+pi+et. The simulation showed Goodwin's model of high- and low-skilled workers produced the ideal of Goodwin model cycle predictions, whereas Goodwin's model of medium-skilled workers and the entire economy (capitalist) didn’t produce the ideal of Goodwin model cycle predictions. Eventually, the effects of reducing the wage gap make the economy unstable.
Published in Cauchy (SINTA 2)
A discrete-time fractional-order Rosenzweig-Macarthur predator-prey model involving prey refuge
Author: Hasan S. Panigoro, Emli Rahmi, Novianita Achmad, Sri Lestari Mahmud, R. Resmawan, Agusyarif Rezka Nuha
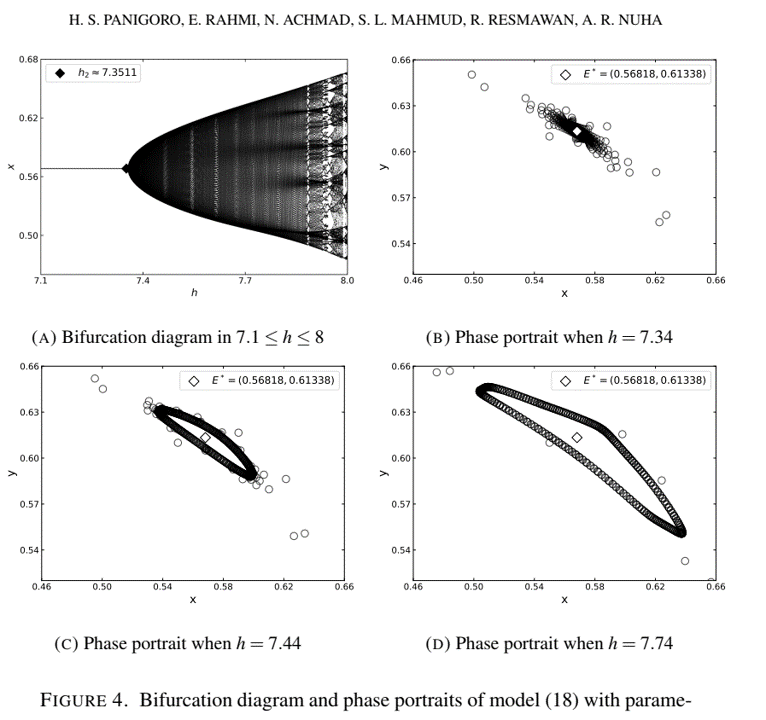
In this article, the dynamical behaviors of a discrete-time fractional-order Rosenzweig-MacArthur model with prey refuge are studied. The piecewise constant arguments scheme is applied to obtain the discrete-time model. All possible fixed points and their existence conditions are investigated as well as the local behavior of nearby solutions in various contingencies. Numerical simulations such as the time series, phase portraits, and bifurcation diagrams are portrayed. Three types of bifurcations are shown numerically namely the forward, the period-doubling, and Neimark-Sacker bifurcations. Some phase portraits are depicted to justify the occurrence of those bifurcations.
Published in Communications in Mathematical Biology and Neuroscience (Q3)
Analysis of The Rosenzweig-MacArthur Predator-Prey Model with Anti-Predator Behavior
Author: Ismail Djakaria, Muhammad Bachtiar Gaib, Resmawan Resmawan
This paper discusses the analysis of the Rosenzweig-MacArthur predator-prey model with anti-predator behavior. The analysis is started by determining the equilibrium points, existence, and conditions of the stability. Identifying the type of Hopf bifurcation by using the divergence criterion. It has shown that the model has three equilibrium points, i.e., the extinction of population equilibrium point (E0), the non-predatory equilibrium point (E1), and the co-existence equilibrium point (E2). The existence and stability of each equilibrium point can be shown by satisfying several conditions of parameters. The divergence criterion indicates the existence of the supercritical Hopf-bifurcation around the equilibrium point E2. Finally, our model's dynamics population is confirmed by our numerical simulations by using the 4th-order Runge-Kutta methods.
Kategori
Arsip
- July 2023 (3)
- January 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (1)
- August 2022 (1)
- July 2022 (6)
- March 2022 (1)
- September 2021 (2)
- October 2020 (1)
- July 2020 (2)
- April 2020 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (1)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- February 2019 (1)
- September 2018 (2)
- August 2018 (1)
- July 2018 (4)
- June 2018 (5)
- September 2017 (2)
- August 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (1)
- October 2016 (1)
- September 2016 (2)
- September 2015 (4)
- June 2015 (1)
Blogroll
- 01 Sistem Informasi Akademik
- 02 Repository UNG
- 03 Universitas Negeri Gorontalo
- 04 Beasiswa DIKTI
- 05 Beasiswa LPDP
- 06 BookFi
- 07 Indonesian Mathematical Society
- 08 EBSCOhost
- 09 Library Genesis
- 10 Khan Academy
- 11 Blog Pribadi
- 12 Twitter
- 13 Facebook
- 14 Pdf Drive
- 15 Pangkalan Data UNG
- 16 Differential Equation
- 17 Math is Fun
- 18 Jambura Journal of Mathematics
- 19 OSF
- 20 Sci-Hub
- 21 Researchsquare
- 22 Kalkulator Math
- 23 Gometa
- 24 Microsite
- 25 Wordwall
- 26 Science Direct
- 27 BSRE BSSN
- 28 OpenAI
- 29 Quillbot
- 30 Perplexity
- 31 Citation FInder
