Sensitivity Analysis of Mathematical Model of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Transmission
Coronavirus Disease (henceforth, COVID-19) has shocked many thanks to its very rapid spread. Firstly, identified to occur in Wuhan city of China, the disease has shortly become one of the main talking points as it reached the whole world and took thousands of death tolls in a very short period. The disease somewhat instigates all parties to conduct active measures in finding options to the best treatments and anticipatory means to prevent damage on a much wider scale. From a mathematical perspective, the concern is closely related to the implementation of mathematical models to identify potential solutions.
Mathematical modeling is one of the key tools in epidemic preparation, including the COVID-19 pandemic. The system allows one to comprehend and identify the correlation between COVID-19 spread and several epidemiology parameters, conduct preparatory measures for future planning, and implement best practices of pandemic treatment. Previous studies, albeit little in number, have begun to address this problem and design mathematical model for COVID-19 transmission [1][2][3][4]. The model involved accurate and effective public health interventions. On top of that, a study comparedbetween the outbreaks of current COVID-19 and previous MERS disease that spread in Middle Eastern countries and Korea [5]. Other studies designed mathematical models that predict COVID-19 cases in different countries [6][7].
Several models proposed in previous studies have discussed that the virus started from an unknown source and eventually began to spread to the human population. The virus source, further referred to as reservoir variable, is suspected to be the place of first infection-to-human case. The present study introduces a different approach to mathematical modeling to the virus transmission by also involving the epidemiology parameters; a variable that is not discussed in previous studies. Previous models have assumed that the virus transmission only occurs in interactions between individuals that have contracted the virus; differing from that, this article takes into consideration transmission cases caused by susceptible individuals and exposed individuals. It views the importance of involving such parameters, considering the number of infections that occurred in the interaction between exposed individuals yet to be detected as infected. Moreover, the model lays its emphasis on the pattern of transmission between humans after the virus has become epidemic or pandemic, therefore, disregarding the reservoir variable. The model thus overlooks the process of first human infection and focuses on how the virus has spread within human-to-human interactions. In addition to that, the model employs new parameters representing death cases of COVID-19, pertaining to the fact that the virus has taken numbers of the death tolls. The model also takes into account cases of quarantined individuals that were identified to be exposed to the virus.
The following section elaborates on the construction of mathematical models in this study. Further, the article presents the research results in the form of model analysis. Within this section, the study focuses on the construction of basic reproductive number and sensitivity analysis to identify which parameter is the most sensitive to the change in basic reproductive number value. Finally, the last section proposes several conclusions to the research findings and discussion.
Analisis Kestabilan Model Predator-Prey dengan Infeksi Penyakit pada Prey dan Pemanenan Proporsional pada Predator
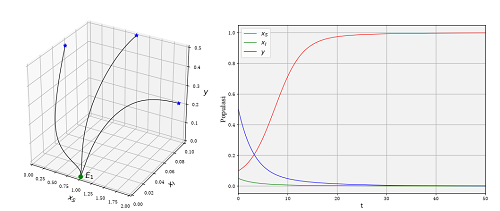 |
Pemodelan matematika merupakan cabang ilmu matematika yang merepresentasikan atau menjelaskan masalah di kehidupan nyata kedalam bentuk matematika. Pemodelan matematika biasanya selalu dikaitkan dengan cabang ilmu yang lain seperti biologi, fisika, kesehatan, dan teknik [1]. Salah satu cabang ilmu biologi adalah ekologi. Ekologi adalah ilmu yang mempelajari makhluk hidup dan interaksinya terhadap lingkungan maupun interaksi dengan sesama makhluk hidup [2]. Pada dasarnya model matematika dalam bidang ekologi merupakan studi tentang keterkaitan antara spesies dan lingkungannya, dalam bidang-bidang seperti interaksi pemangsa dan persaingan. Salah satu model matematika dalam bidang ekologi adalah model predator-prey.odel Lotka-Voltera adalah model predator-prey yang paling sederhana [3]. Berdasarkan model tersebut, dapat diketahui bahwa kedua spesies saling mempengaruhi satu sama lain, apabila terdapat spesies mangsa yang berlimpah, maka populasi pemangsa juga terus meningkat. Model Lotka-Voltera mengasumsikan laju pertumbuhan prey dan predator bertumbuh secara eksponensial. Kemudian pada tahun 1934, Gause mengembangkan model Lotka-Voltera [4], pada model Gause tersebut laju pertumbuhan prey diasumsikan bertumbuh secara logistik dan pertumbuhan predator bertumbuh secara eksponensial [5]. Kajian tentang model predator-prey merupakan hal yang sangat menarik sehingga sampai saat ini masih terus dipelajari dandikembangkan seperti di [6–13].
Selain model ekologi, masalah epidemiologi merupakan salah satu topik hangat dalam pemodelan matematika. Pemodelan matematika dalam epidemiologi memberikan pemahaman tentang mekanisme mendasar yang mempengaruhi penyebaran penyakit. Dalam pemodelan matematika dari penularan penyakit, seperti di sebagian besar bidang pemodelan matematika lain, biasanya dilakukan modifikasi antara model-model sederhana, yang menghilangkan sebagian detail dan merancang untuk memodelkan perilaku kualitatif umum, dan model kompleks, biasanya dirancang untuk situasi tertentu [14].
Pada beberapa tahun terakhir penelitian akan ekologi dan epidemiologi banyak dilakukan, meski dua bidang ini berbeda kontribusinya terhadap ilmu pengetahuan namun ada kesamaan diantara keduanya yaitu mencakup makhluk hidup. Model yang diangkat pada artikel ini merupakan gabungan kajian dari model Ekologi dan model Epidemiologi yang disebut dengan model Eko-epidemiologi. Beberapa peneliti telah mempelajari model eko-epidemiologi seperti pada [1, 15–21]. Artikel ini mempelajari model yang serupa dengan model dalam penelitian Panigoro dkk. [20] yaitu model eko-epidemiologi dengan mengasumsikan bahwa prey tumbuh logistik dan predator tumbuh secara eksponensial dengan adanya infeksi penyakit pada prey. Namun fungsi respon yang digunakan pada model penelitian [20] mengikuti Holling Tipe II sedangkan pada penelitian ini menggunakan fungsi respon Holling Tipe I. Selanjutnya pada beberapa kondisi yang terjadi di alam memperlihatkan terjadinya perburuan terhadap spesies predator oleh manusia. Oleh karena itu, model ini dimodifikasi dengan menambahkan asumsi bahwa terjadi pemanenan terhadap predator, yang berdasarkan kajian literatur penulis, model dengan modifikasi ini belum pernah dipelajari sebelumnya. Meskipun modifikasi yang dilakukan cukup sederhana, namun hasil analisis memperlihatkan bahwa terjadi perubahan signifikan pada dinamika dari model dibandingkan model rujukan. Eksistensi dan kestabilan dari model sangatbergantung pada besarnya pemanenan yang dilakukan. Hal inilah yang akan ditunjukkan dalam artikel ini.
Kategori
Arsip
- July 2023 (3)
- January 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (1)
- August 2022 (1)
- July 2022 (6)
- March 2022 (1)
- September 2021 (2)
- October 2020 (1)
- July 2020 (2)
- April 2020 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (1)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- February 2019 (1)
- September 2018 (2)
- August 2018 (1)
- July 2018 (4)
- June 2018 (5)
- September 2017 (2)
- August 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (1)
- October 2016 (1)
- September 2016 (2)
- September 2015 (4)
- June 2015 (1)
Blogroll
- 01 Sistem Informasi Akademik
- 02 Repository UNG
- 03 Universitas Negeri Gorontalo
- 04 Beasiswa DIKTI
- 05 Beasiswa LPDP
- 06 BookFi
- 07 Indonesian Mathematical Society
- 08 EBSCOhost
- 09 Library Genesis
- 10 Khan Academy
- 11 Blog Pribadi
- 12 Twitter
- 13 Facebook
- 14 Pdf Drive
- 15 Pangkalan Data UNG
- 16 Differential Equation
- 17 Math is Fun
- 18 Jambura Journal of Mathematics
- 19 OSF
- 20 Sci-Hub
- 21 Researchsquare
- 22 Kalkulator Math
- 23 Gometa
- 24 Microsite
- 25 Wordwall
- 26 Science Direct
- 27 BSRE BSSN
- 28 OpenAI
- 29 Quillbot
- 30 Perplexity
- 31 Citation FInder
